Uterine Fibroid Treatment in Thane
What exactly Uterine Fibroid Treatment ?
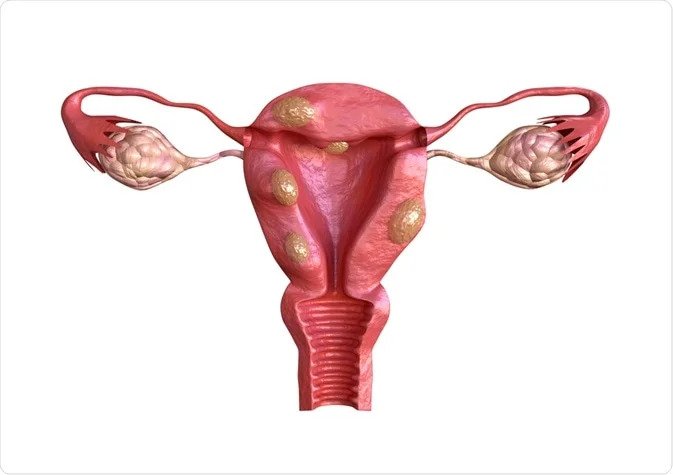
Fibroid tumors are noncancerous growths that form on the muscle wall of the uterus. They might be small or large to occupy the whole abdominal cavity. Women of all ages may be affected by this condition, but women in their 40s and 50s are the most affected. for more information on Uterine Fibroid Treatment consult with our best gynaecologist for fibroids Dr. Arohi.
What Are the Types of Uterine Fibroid?
- Intramural Fibroids – Uterine fibroids usually develop within the uterine wall. These are known as intramural fibroids, and they may reduce womb size.
- Subserosal Fibroids – These subserosal fibroids are found on the exterior of the uterus, which is known as the serosa. In cases where the fibroid is too large, the womb may appear to be larger on one side.
- Pedunculated Fibroids – In case a subserosal fibroid develops a thin base to support the tumor, it is known as a pedunculated fibroid.
- Submucosal Fibroids – These are uterine fibroids that develop in the uterine cavity or myometrium.
Symptoms of Uterine Fibroid
Many women with uterine fibroids have no noticeable symptoms. Depending on the size, quantity, and location of the fibroids, those who have symptoms may encounter the following.
- Heavy menstrual discharge
- Difficulty emptying the bladder
- Constipation
- Menstrual cycles that last longer than a week
- Pelvic discomfort or pressure
- Frequent urination
- Back pain or leg pain
What tests are used to diagnose uterine fibroids?
Certain tests will be recommended by your doctor to confirm the presence of uterine fibroids and to establish their size and location. These include tests like:
- Ultrasonography or Ultrasounds – A non-invasive diagnostic that employs sound waves to create an accurate image of the uterus in order to detect uterine fibroids. The equipment enables the doctor to examine your uterus transabdominally or transvaginally.
- MRI or Magnetic Resonance Imaging – If an ultrasound does not reveal enough images or information, your doctor may advise you to obtain an MRI. If you have a large uterus or are going through menopause, an MRI is also indicated. The test uses radio waves and magnets to reveal detailed images.
- CT Scan or Computed Tomography (CT Scan) – X-ray images are utilized to provide a detailed image of the uterus from various perspectives.
- Hysterosonography – Finding submucosal fibroids is difficult, but this test can help diagnose these cases.
- Hysterosalpingography – A dye is applied to better observe the uterus and check the Fallopian Tubes.
- Hysteroscopy is inserting a small telescope with light into the cervix after enlarging the uterine chamber with a saline solution.
- Laparoscopy – This test is minimally invasive but it is safe. To examine the uterus carefully, the doctor will introduce a laparoscope via a small incision in the abdomen.
Can fibroids develop into cancer?
Fibroids are not medically threatening, although they may turn malignant in certain circumstances. According to statistics, fewer than one in every 1000 women with uterine fibroids would acquire cancerous fibroids.
How long does recovery from Uterine Fibroids take?
Generally, Uterine Fibroids do not have any risks or lead to further complications. As a result, most women do not have uterine fibroids surgically removed. In certain situations, menopause or the stability of hormone levels results in the removal of uterine fibroids.
What are the consequences of not treating uterine fibroids?
Uterine fibroids are painless, although their growth and condition must be closely monitored. If untreated, uterine fibroids may develop and cause complications such as anemia, severe menstrual cramps, and excessive bleeding.
What are the best Uterine Fibroids medications?
Your doctor may recommend drugs to treat your symptoms and limit the likelihood of additional issues. Some well-known pharmaceuticals are: OTC medications – Over-the-counter medications may help control fibroids-related symptoms such as stomach and lower back discomfort.
Hormonal Birth Control Pills – Birth control pills may help balance one’s hormonal levels, reducing the possibility of fibroid development.
Iron Supplements – If you have a lot of bleeding, taking iron supplements might help you avoid anemia.
Gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) agonists – These drugs are used to reduce fibroids before they are removed.
What surgical procedures are used to treat for Uterine Fibroid Treatment?
The following are the various surgical techniques for uterine fibroids:
- Myomectomy – A surgical procedure that removes uterine fibroids without damaging the uterus. It is further subdivided into the following categories:
- Hysteroscopy is inserting a scope into the uterus without making any incisions in order to remove the fibroids.
- Laparoscopy – A scope is inserted through some small incisions on the abdomen.
Laparotomy – An abdominal incision is made and the fibroids are removed in one large cut. - Hysterectomy – The removal of the uterus to treat uterine fibroids permanently.
Embolization of Uterine Fibroids – A catheter is used to limit blood flow and shrink the fibroids. - Radiofrequency ablation is a non-invasive and effective treatment for uterine fibroids and accompanying symptoms.