Best gynecologist for ovarian cyst in Thane
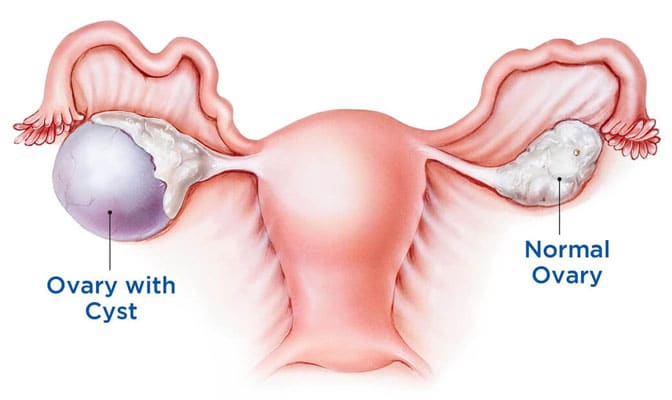
What is Ovarian cyst?
Ovarian cysts are liquid-filled sacs that develop in the ovaries. They are usually painless and have no effect on fertility when they are small, but they worsen with time. To know more about Ovarian cyst consult with our Best gynecologist for ovarian cyst in Thane, Dr. Arohi Tasgaonkar.
Ovarian cyst symptoms
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Bloating or swelling in the abdomen
- Breast tenderness
- Sharp or severe pelvic discomfort
- Increased menstrual pain
- Constipation
- Backache
- Dizziness
Complications arise from an Ovarian Cyst
Doctors may detect certain less common forms of cysts during a pelvic exam. Ovarian cysts that develop after menopause may be malignant, therefore it’s important to undergo frequent pelvic exams. The risks connected with ovarian cysts include:
- Ovarian torsion may reduce or stop blood flow to the ovaries and, if left untreated, can cause ovarian tissue damage.
- Cyst Rupture – When a cyst ruptures, it produces severe pain and internal bleeding. This increases the risk of infection and, if untreated, may be fatal.
- Ovarian Cyst Infection – Although ovarian cysts are benign, ruptured cysts, which are uncommon, may cause discomfort and possibly ovary hemorrhage. This ruptured cyst consequence may raise the risk of infection and should not be ignored
Ovarian cyst diagnosis
- Pelvic Exam – During a pelvic exam, a doctor uses an instrument to enlarge the vagina and examine the vagina, cervix, uterus, and other reproductive organs for abnormalities or lumps.
- Ultrasound – If doctors find any cyst manually, they will request an ultrasound which helps to understand the size, shape, location and composition (solid or fluid-filled) of the cyst.
- Pregnancy Test – Doctor may also prescribe a pregnancy test, and a positive result may indicate the existence of a corpus luteum cyst.
- CA 125 Blood Test – A doctor may prescribe a CA 125 blood test if the cyst is partly solid and the patient is at a greater risk of ovarian cancer. Cancer antigen 125 (CA 125) protein levels in the blood are often high in ovarian cancer patients. Non-cancerous diseases such as endometriosis, uterine fibroids, and pelvic inflammatory disease have high CA 125 levels.
- Other Blood Tests – If a woman is under the age of 40, the doctor may order additional blood tests such as LDH (lactate dehydrogenase), AFP (alpha-fetoprotein), and HCG (human chorionic gonadotropin), which are all tumor markers to determine whether the cyst is a type of cancer known as a germ cell tumor, which is extremely rare.
- CT Scan – A type of body imaging technology that produces cross-sectional pictures of interior organs. CT scans cannot detect small ovarian tumors, but they may detect large tumors and determine if the tumor is expanding into surrounding tissues. It may also detect swollen lymph nodes, symptoms of cancer spread to the liver or other organs, and if an ovarian tumor is impacting the kidney or bladder.
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a technique that employs magnetic fields to provide detailed pictures of interior organs. If a doctor finds the cyst as a solid mass, then might advise an MRI.
Ovarian cyst treatment
- Watchful Waiting – Because the majority of cysts resolve over a few weeks or months, a doctor may not propose a treatment strategy immediately. If there are no symptoms and an ultrasound report reveals merely a small fluid-filled cyst, it is best to wait and monitor, and re-examine whether required, to see if the cyst has disappeared on its own.
- Birth Control Pills – If an ovarian cyst reappears, the doctor may prescribe oral contraceptive pills to prevent ovulation and the development of additional cysts.
- Laparoscopy is a surgical technique in which a doctor inserts a small instrument via an incision in the abdomen. Using this instrument, the doctor may examine the reproductive organs and pelvic cavity.
- Laparotomy – If the cyst is more than 5 cm in size, the doctor will surgically remove it via a major incision in the abdomen. They will next do a biopsy, and if the cyst is found to be cancerous, they will perform a hysterectomy to remove the ovaries and uterus.
For more information & consultation on ovarian cyst in Thane, visit Complete Women’s Care at Ghodbunder road, Thane or contact us on 9833074977 or simply fill in your name and number & one of our team member will get in touch with you soon. Our team of experts along with Dr. Arohi Tasgaonkar, MS (ObGy), DNB (ObGy), and one of the Best gynecologist for ovarian cyst in Thane will help you out in understanding your problem and guide you through every stage of your treatment.